Option Strategies
Naked Call
Introduction
A Naked Call, also known as an uncovered call, consists of selling call Options without owning the underlying asset. It's called "naked" because you don't have any cover or protection in the form of owning the underlying asset, which exposes you to potentially unlimited risk. Naked calls aim to profit from the Option premium by selling calls. At any time for American Options or at expiration for European Options, if the stock moves below the strike price, you keep the premium. If the underlying price moves above the strike, the Option buyer can exercise the Options contract, which means you need buy the underlying at market price to fulfill your obligation to sell it at the strike price and keep the premium.
Implementation
Follow these steps to implement the naked call strategy:
- In the
Initializeinitializemethod, set the start date, end date, starting cash, and Options universe. - In the
OnDataon_datamethod, select the Option contract. - In the
OnDataon_datamethod, place the orders.
private Symbol _call, _symbol;
public override void Initialize()
{
SetStartDate(2024, 9, 1);
SetEndDate(2024, 12, 31);
SetCash(100000);
UniverseSettings.Asynchronous = true;
var option = AddOption("IBM");
_symbol = option.Symbol;
option.SetFilter(universe => universe.IncludeWeeklys().NakedCall(30, 0));
} def initialize(self) -> None:
self.set_start_date(2024, 9, 1)
self.set_end_date(2024, 12, 31)
self.set_cash(100000)
self.universe_settings.asynchronous = True
option = self.add_option("IBM")
self._symbol = option.symbol
option.set_filter(lambda universe: universe.include_weeklys().naked_call(30, 0))
The NakedCallnaked_call filter narrows the universe down to just the one contract you need to form a naked call.
public override void OnData(Slice slice)
{
if (Portfolio.Invested ||
!slice.OptionChains.TryGetValue(_symbol, out var chain)) return;
// Find ATM call with the farthest expiry
var expiry = chain.Max(x => x.Expiry);
var atmCall = chain
.Where(x => x.Right == OptionRight.Call && x.Expiry == expiry)
.OrderBy(x => Math.Abs(x.Strike - chain.Underlying.Price))
.FirstOrDefault(); def on_data(self, slice: Slice) -> None:
if self.portfolio.invested:
return
chain = slice.option_chains.get(self._symbol)
if not chain:
return
# Find ATM call with the farthest expiry
expiry = max([x.expiry for x in chain])
call_contracts = sorted([x for x in chain
if x.right == OptionRight.CALL and x.expiry == expiry],
key=lambda x: abs(chain.underlying.price - x.strike))
if not call_contracts:
return
atm_call = call_contracts[0]
Approach A: Call the OptionStrategies.NakedCallOptionStrategies.naked_call method with the details of each leg and then pass the result to the Buybuy method.
var nakedCall = OptionStrategies.NakedCall(_symbol, atmCall.Strike, expiry); Buy(nakedCall, 1);
naked_call = OptionStrategies.naked_call(self._symbol, atm_call.strike, expiry) self.buy(naked_call, 1)
Approach B: Call the Market Ordermarket_order or Limit Orderlimit_order method.
MarketOrder(atmCall.Symbol, -1);
self.market_order(atm_call.symbol, -1)
Strategy Payoff
The payoff of the strategy is
$$ \begin{array}{rcll} C^{K}_T & = & (S_T - K)^{+}\\ P_T & = & (C^{K}_0 - C^{K}_T)\times m - fee \end{array} $$ $$ \begin{array}{rcll} \textrm{where} & C^{K}_T & = & \textrm{Call value at time T}\\ & S_T & = & \textrm{Underlying asset price at time T}\\ & K & = & \textrm{Call strike price}\\ & P_T & = & \textrm{Payout total at time T}\\ & C^{K}_0 & = & \textrm{Call price when the trade opened (credit received)}\\ & m & = & \textrm{Contract multiplier}\\ & T & = & \textrm{Time of expiration} \end{array} $$The following chart shows the payoff at expiration:
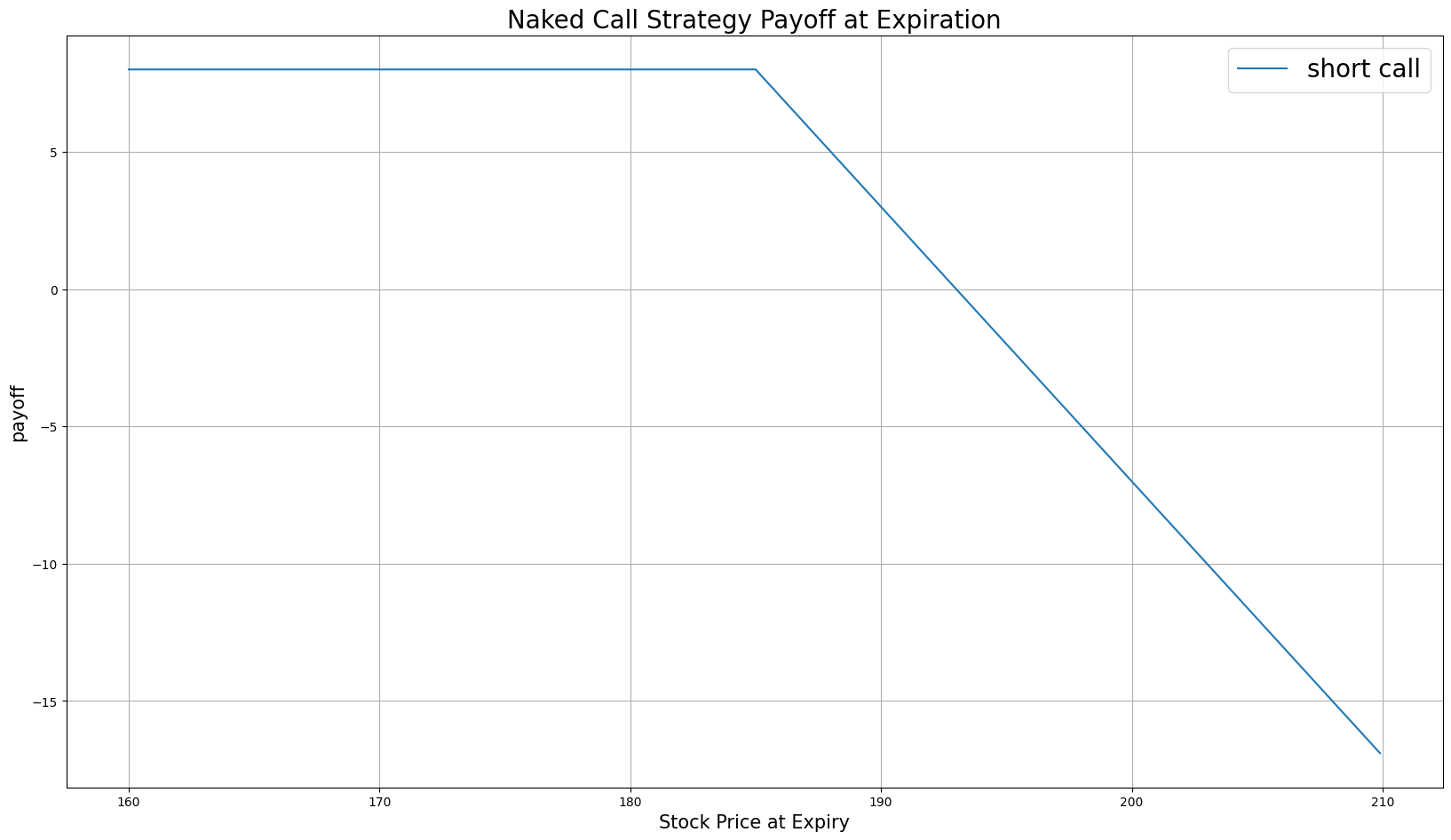
The maximum profit is $C^{K}_0$, which occurs when the underlying price is at or below the strike price of the call at expiration.
The maximum loss is unlimited because there is no limit to how high the underlying asset's price can rise.
If the Option is American Option, there is a risk of early assignment on the contract you sell.
Example
The following table shows the price details of the assets in the algorithm:
| Asset | Price ($) | Strike ($) |
|---|---|---|
| Call | 3.35 | 185.00 |
| Underlying Equity at expiration | 190.01 | - |
Therefore, the payoff is
$$ \begin{array}{rcll} C^{K}_T & = & (S_T - K)^{+}\\ & = & (190.01 - 185)^{+}\\ & = & 5.01\\ P_T & = & (C^{K}_0 - C^{K}_T)\times m - fee\\ & = & (3.35 - 5.01)\times m - fee\\ & = & -1.66 \times 100 - 2\\ & = & -167 \end{array} $$So, the strategy loses $167.
The following algorithm implements a naked call Option strategy:
public class NakedCallAlgorithm : QCAlgorithm
{
private Symbol _call, _symbol;
public override void Initialize()
{
SetStartDate(2024, 9, 1);
SetEndDate(2024, 12, 31);
SetCash(100000);
var option = AddOption("IBM");
_symbol = option.Symbol;
option.SetFilter(universe => universe.IncludeWeeklys().NakedCall(30, 0));
// use the underlying equity as the benchmark
SetBenchmark(_symbol.Underlying);
}
public override void OnData(Slice slice)
{
if (_call != null && Portfolio[_call].Invested) return;
if (!slice.OptionChains.TryGetValue(_symbol, out var chain)) return;
// Find ATM call with the farthest expiry
var expiry = chain.Max(x => x.Expiry);
var atmCall = chain
.Where(x=> x.Right == OptionRight.Call && x.Expiry == expiry)
.OrderBy(x => Math.Abs(x.Strike - chain.Underlying.Price))
.FirstOrDefault();
if (atmCall == null) return;
var nakedCall = OptionStrategies.NakedCall(_symbol, atmCall.Strike, expiry);
Buy(nakedCall, 1);
_call = atmCall.Symbol;
}
} class NakedCallAlgorithm(QCAlgorithm):
def initialize(self) -> None:
self.set_start_date(2024, 9, 1)
self.set_end_date(2024, 12, 31)
self.set_cash(100000)
option = self.add_option("IBM")
self.symbol = option.symbol
option.set_filter(lambda universe: universe.include_weeklys().naked_call(30, 0))
self.call = None
# use the underlying equity as the benchmark
self.set_benchmark(self.symbol.underlying)
def on_data(self, slice: Slice) -> None:
if self.call and self.portfolio[self.call].invested:
return
chain = slice.option_chains.get(self.symbol)
if not chain:
return
# Find ATM call with the farthest expiry
expiry = max([x.expiry for x in chain])
call_contracts = sorted([x for x in chain
if x.right == OptionRight.CALL and x.expiry == expiry],
key=lambda x: abs(chain.underlying.price - x.strike))
if not call_contracts:
return
atm_call = call_contracts[0]
naked_call = OptionStrategies.naked_call(self.symbol, atm_call.strike, expiry)
self.buy(naked_call, 1)
self.call = atm_call.symbol