CFD
Handling Data
Introduction
LEAN passes the data you request to the OnDataon_data method so you can make trading decisions. The default OnDataon_data method accepts a Slice object, but you can define additional OnDataon_data methods that accept different data types. For example, if you define an OnDataon_data method that accepts a QuoteBar argument, it only receives QuoteBar objects. The Slice object that the OnDataon_data method receives groups all the data together at a single moment in time. To access the Slice outside of the OnDataon_data method, use the CurrentSlicecurrent_slice property of your algorithm.
All the data formats use DataDictionary objects to group data by Symbol and provide easy access to information. The plural of the type denotes the collection of objects. For instance, the QuoteBars DataDictionary is made up of QuoteBar objects. To access individual data points in the dictionary, you can index the dictionary with the CFD ticker or Symbolsymbol, but we recommend you use the Symbolsymbol.
To view the resolutions that are available for CFD data, see Resolutions.
Quotes
QuoteBar objects are bars that consolidate NBBO quotes from the exchanges. They contain the open, high, low, and close prices of the bid and ask. The Openopen, Highhigh, Lowlow, and Closeclose properties of the QuoteBar object are the mean of the respective bid and ask prices. If the bid or ask portion of the QuoteBar has no data, the Openopen, Highhigh, Lowlow, and Closeclose properties of the QuoteBar copy the values of either the Bidbid or Askask instead of taking their mean.
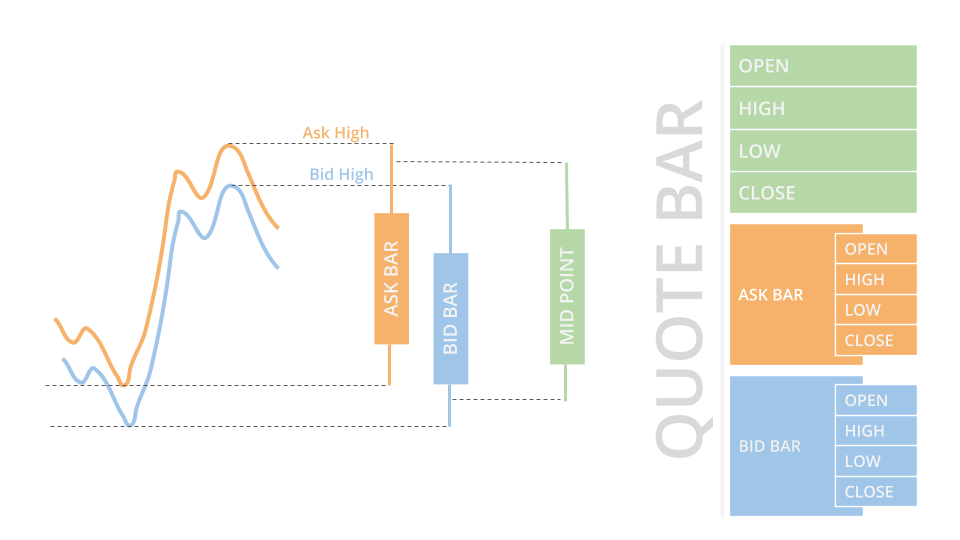
To get the QuoteBar objects in the Slice, index the QuoteBars property of the Slice with the CFD Symbolsymbol. If the CFD doesn't actively get quotes or you are in the same time step as when you added the CFD subscription, the Slice may not contain data for your Symbolsymbol. To avoid issues, check if the Slice contains data for your CFD before you index the Slice with the CFD Symbolsymbol.
public override void OnData(Slice slice)
{
// Check if the symbol is contained in QuoteBars object
if (slice.QuoteBars.ContainsKey(_symbol))
{
// Obtain the mapped QuoteBar of the symbol
var quoteBar = slice.QuoteBars[_symbol];
}
}
def on_data(self, slice: Slice) -> None:
# Obtain the mapped QuoteBar of the symbol if any
quote_bar = slice.quote_bars.get(self._symbol) # None if not found
You can also iterate through the QuoteBars dictionary. The keys of the dictionary are the Symbol objects and the values are the QuoteBar objects.
public override void OnData(Slice slice)
{
// Iterate all received Symbol-QuoteBar key-value pairs
foreach (var kvp in slice.QuoteBars)
{
var symbol = kvp.Key;
var quoteBar = kvp.Value;
var askPrice = quoteBar.Ask.Close;
}
} def on_data(self, slice: Slice) -> None:
# Iterate all received Symbol-QuoteBar key-value pairs
for symbol, quote_bar in slice.quote_bars.items():
ask_price = quote_bar.ask.close
QuoteBar objects let LEAN incorporate spread costs into your simulated trade fills to make backtest results more realistic.
QuoteBar objects have the following properties:
Ticks
Tick objects represent a single trade or quote at a moment in time. A trade tick is a record of a transaction for the CFD. A quote tick is an offer to buy or sell the CFD at a specific price.
Trade ticks have a non-zero value for the Quantityquantity and Priceprice properties, but they have a zero value for the BidPricebid_price, BidSizebid_size, AskPriceask_price, and AskSizeask_size properties. Quote ticks have non-zero values for BidPricebid_price and BidSizebid_size properties or have non-zero values for AskPriceask_price and AskSizeask_size properties. To check if a tick is a trade or a quote, use the TickTypeticktype property.
In backtests, LEAN groups ticks into one millisecond buckets. In live trading, LEAN groups ticks into ~70-millisecond buckets. To get the Tick objects in the Slice, index the Ticks property of the Slice with a Symbolsymbol. If the CFD doesn't actively trade or you are in the same time step as when you added the CFD subscription, the Slice may not contain data for your Symbolsymbol. To avoid issues, check if the Slice contains data for your CFD before you index the Slice with the CFD Symbolsymbol.
public override void OnData(Slice slice)
{
if (slice.Ticks.ContainsKey(_symbol))
{
var ticks = slice.Ticks[_symbol];
foreach (var tick in ticks)
{
var price = tick.Price;
}
}
}
def on_data(self, slice: Slice) -> None:
ticks = slice.ticks.get(self._symbol, []) # Empty if not found
for tick in ticks:
price = tick.price
You can also iterate through the Ticks dictionary. The keys of the dictionary are the Symbol objects and the values are the List<Tick>list[Tick] objects.
public override void OnData(Slice slice)
{
foreach (var kvp in slice.Ticks)
{
var symbol = kvp.Key;
var ticks = kvp.Value;
foreach (var tick in ticks)
{
var price = tick.Price;
}
}
} def on_data(self, slice: Slice) -> None:
for symbol, ticks in slice.ticks.items():
for tick in ticks:
price = tick.price
Tick data is raw and unfiltered, so it can contain bad ticks that skew your trade results. For example, some ticks come from dark pools, which aren't tradable. We recommend you only use tick data if you understand the risks and are able to perform your own online tick filtering.
Tick objects have the following properties:
Examples
The following examples demonstrate common practices for handling CFD data.
Example 1: Buy And Hold
The following algorithm is a buy-and-hold strategy on the DE30EUR CFD contract. We only place orders when quote data is available to avoid stale fills. Also, we set the algorithm time zone to Berlin and the account currency to Euros for a more convenient comparison.
public class CfdExampleAlgorithm : QCAlgorithm
{
private Symbol _dax, _sgx;
public override void Initialize()
{
SetStartDate(2024, 9, 1);
SetEndDate(2024, 12, 31);
// Set the timezone as Berlin to conveniently compare the data.
SetTimeZone(TimeZones.Berlin);
// Set the account currency to EUR to trade the DAX CFD.
SetAccountCurrency("EUR", 10000);
// Request the CFD data to trade.
_dax = AddCfd("DE30EUR").Symbol;
_sgx = AddCfd("SG30SGD").Symbol;
}
public override void OnData(Slice slice)
{
// Trade based on updated data; CFDs only have quote data.
if (slice.QuoteBars.TryGetValue(_dax, out var _))
{
// Buy and hold DAX CFD.
if (!Portfolio[_dax].IsLong)
{
SetHoldings(_dax, 0.5m);
}
}
}
} class CfdExampleAlgorithm(QCAlgorithm):
def initialize(self) -> None:
self.set_start_date(2024, 9, 1)
self.set_end_date(2024, 12, 31)
# Set the timezone as Berlin to conveniently compare the data.
self.set_time_zone(TimeZones.BERLIN)
# Set the account currency to EUR to trade the DAX CFD.
self.set_account_currency("EUR", 10000)
# Request the CFD data to trade.
self._dax = self.add_cfd("DE30EUR").symbol
def on_data(self, slice: Slice) -> None:
# Trade based on updated data; CFDs only have quote data.
bar = slice.quote_bars.get(self._dax)
if bar:
# Buy and hold DAX CFD.
if not self.portfolio[self._dax].is_long:
self.set_holdings(self._dax, 0.5)
Example 2: Global Indices
The following algorithm buys and holds various Index CFDs that trade in different market hours and currencies during their opening hours.
public class CfdExampleAlgorithm : QCAlgorithm
{
public override void Initialize()
{
SetStartDate(2024, 9, 1);
SetEndDate(2024, 12, 31);
// Seed the price of each asset with its last known price to
// avoid trading errors.
Settings.SeedInitialPrices = true;
// Let's select CFD contracts that trade in different market
// hours so the algorithm is always invested.
foreach (var ticker in new[] { "DE30EUR", "SG30SGD", "US30USD" })
{
// Add the CFD.
var symbol = AddCfd(ticker).Symbol;
// Set scheduled events to hold each CFD contract during
// their regular trading hours.
// Buy after market open.
Schedule.On(
DateRules.EveryDay(symbol),
TimeRules.AfterMarketOpen(symbol, 1),
() => SetHoldings(symbol, 0.3m)
);
// Liquidate before market close.
Schedule.On(
DateRules.EveryDay(symbol),
TimeRules.BeforeMarketClose(symbol, 1),
() => Liquidate(symbol)
);
}
}
} class CfdExampleAlgorithm(QCAlgorithm):
def initialize(self) -> None:
self.set_start_date(2024, 9, 1)
self.set_end_date(2024, 12, 31)
# Seed the price of each asset with its last known price to
# avoid trading errors.
self.settings.seed_initial_prices = True
# Let's select CFD contracts that trade in different market
# hours so the algorithm is always invested.
for ticker in ['DE30EUR', 'SG30SGD', 'US30USD']:
# Add the CFD.
symbol = self.add_cfd(ticker).symbol
# Set scheduled events to hold each CFD contract during
# their regular trading hours.
# Buy after market open.
self.schedule.on(
self.date_rules.every_day(symbol),
self.time_rules.after_market_open(symbol, 1),
lambda symbol=symbol: self.set_holdings(symbol, 0.3)
)
# Liquidate before market close.
self.schedule.on(
self.date_rules.every_day(symbol),
self.time_rules.before_market_close(symbol, 1),
lambda symbol=symbol: self.liquidate(symbol)
)