Popular Libraries
TensorFlow
Get Historical Data
Get some historical market data to train and test the model. For example, to get data for the SPY ETF during 2020 and 2021, run:
qb = QuantBook() symbol = qb.add_equity("SPY", Resolution.DAILY).symbol history = qb.history(symbol, datetime(2020, 1, 1), datetime(2022, 1, 1)).loc[symbol]
Prepare Data
You need some historical data to prepare the data for the model. If you have historical data, manipulate it to train and test the model. In this example, use the following features and labels:
| Data Category | Description |
|---|---|
| Features | The last 5 close price differencing to the current price |
| Labels | The following day's price change |
Follow these steps to prepare the data:
- Loop through the DataFrame of historical prices and collect the features.
- Select the close column and then call the
shiftmethod to collect the labels. - Drop the first 5 samples and then call the
reset_indexmethod. - Split the data into training and testing datasets.
data = history lookback = 5 lookback_series = [] for i in range(1, lookback + 1): df = data['close'].diff(i)[lookback:-1] df.name = f"close-{i}" lookback_series.append(df) X = pd.concat(lookback_series, axis=1).reset_index(drop=True).dropna() X
The following image shows the format of the features DataFrame:
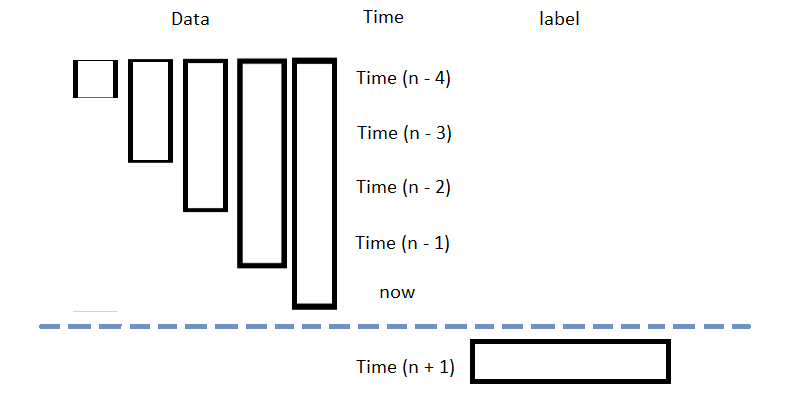
Y = data['close'].diff(-1)
Y = Y[lookback:-1].reset_index(drop=True)
This method aligns the history of the features and labels.
For example, to use the last third of data to test the model, run:
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X, Y, test_size=0.33, shuffle=False)
Train Models
You need to prepare the historical data for training before you train the model. If you have prepared the data, build and train the model. In this example, build a neural network model that predicts the future price of the SPY.
Build the Model
Follow these steps to build the model:
- Set the number of layers, their number of nodes, the number of epoch and the learning rate.
- Create hidden layers with the set number of layer and their corresponding number of nodes.
- Select an optimizer.
- Define the loss function.
num_factors = X_test.shape[1] num_neurons_1 = 10 num_neurons_2 = 10 num_neurons_3 = 5 epochs = 20 learning_rate = 0.0001
In this example, we're constructing the model with the in-built Keras API, with Relu activator for non-linear activation of each tensors.
model = tf.keras.sequential([ tf.keras.layers.dense(num_neurons_1, activation=tf.nn.relu, input_shape=(num_factors,)), # input shape required tf.keras.layers.dense(num_neurons_2, activation=tf.nn.relu), tf.keras.layers.dense(num_neurons_3, activation=tf.nn.relu), tf.keras.layers.dense(1) ])
We're using Adam optimizer in this example. You may also consider others like SGD.
optimizer = tf.keras.optimizers.adam(learning_rate=learning_rate)
In the context of numerical regression, we use MSE as our objective function. If you're doing classification, cross entropy would be more suitable.
def loss_mse(target_y, predicted_y): return tf.reduce_mean(tf.square(target_y - predicted_y))
Train the Model
Iteratively train the model by the set epoch number. The model will train adaptively by the gradient provided by the loss function with the selected optimizer.
for i in range(epochs): with tf.gradient_tape() as t: loss = loss_mse(y_train, model(X_train)) train_loss = loss_mse(y_train, model(X_train)) test_loss = loss_mse(y_test, model(X_test)) print(f"""Epoch {i+1}: Training loss = {train_loss.numpy()}. Test loss = {test_loss.numpy()}""") jac = t.gradient(loss, model.trainable_weights) optimizer.apply_gradients(zip(jac, model.trainable_weights))
Test Models
To test the model, we'll setup a method to plot test set predictions ontop of the SPY price.
def test_model(actual, title, X): prediction = model(X).numpy() prediction = prediction.reshape(-1, 1) plt.figure(figsize=(16, 6)) plt.plot(actual, label="Actual") plt.plot(prediction, label="Prediction") plt.title(title) plt.xlabel("Time step") plt.ylabel("SPY Price") plt.legend() plt.show() test_model(y_test, "Test Set Results from Original Model", X_test)

Store Models
You can save and load TensorFlow models using the Object Store.
Save Models
Follow these steps to save models in the Object Store:
- Set the key name of the model to be stored in the Object Store.
- Call the
get_file_pathmethod with the key. - Call the
savemethod with the model and file path. - Save the model to the file path.
model_key = "model.keras"
Note that the model has to have the suffix .keras.
file_name = qb.object_store.get_file_path(model_key)
This method returns the file path where the model will be stored.
model.save(file_name)
qb.object_store.save(model_key)
Load Models
You must save a model into the Object Store before you can load it from the Object Store. If you saved a model, follow these steps to load it:
- Get the file path from the Object Store.
- Restore the
TensorFlowmodel from the saved path.
file_name = qb.object_store.get_file_path(model_key)
model = tf.keras.models.load_model(file_name)
Examples
The following examples demonstrate some common practices for using the Tensorflow library.
Example 1: Predict Next Return
The following research notebook uses Tensorflow machine learning model to predict the next day's return by the previous 5 days' close price differencing.
# Import the Tensorflow library and others. import tensorflow as tf from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split # Instantiate the QuantBook for researching. qb = QuantBook() # Request the daily SPY history with the date range to be studied. symbol = qb.add_equity("SPY", Resolution.DAILY).symbol history = qb.history(symbol, datetime(2020, 1, 1), datetime(2022, 1, 1)).loc[symbol] # Loop through the DataFrame of historical prices and collect the features. data = history lookback = 5 lookback_series = [] for i in range(1, lookback + 1): df = data['close'].diff(i)[lookback:-1] df.name = f"close-{i}" lookback_series.append(df) X = pd.concat(lookback_series, axis=1).reset_index(drop=True).dropna() # Select the close column and then call the shift method to collect the labels. # This method aligns the history of the features and labels. Y = data['close'].diff(-1) Y = Y[lookback:-1].reset_index(drop=True) # Split the data into training and testing datasets. For example, to use the last third of data to test the model. X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X, Y, test_size=0.33, shuffle=False) # Set the number of layers, their number of nodes, the number of epoch and the learning rate. num_factors = X_test.shape[1] num_neurons_1 = 10 num_neurons_2 = 10 num_neurons_3 = 5 epochs = 20 learning_rate = 0.0001 # Create hidden layers with the set number of layer and their corresponding number of nodes. # In this example, we're constructing the model with the in-built Keras API, with Relu activator for non-linear activation of each tensors. model = tf.keras.sequential([ tf.keras.layers.dense(num_neurons_1, activation=tf.nn.relu, input_shape=(num_factors,)), # input shape required tf.keras.layers.dense(num_neurons_2, activation=tf.nn.relu), tf.keras.layers.dense(num_neurons_3, activation=tf.nn.relu), tf.keras.layers.dense(1) ]) # We're using Adam optimizer in this example. You may also consider others like SGD. optimizer = tf.keras.optimizers.adam(learning_rate=learning_rate) # Define the loss function. In the context of numerical regression, we use MSE as our objective function. If you're doing classification, cross entropy would be more suitable. def loss_mse(target_y, predicted_y): return tf.reduce_mean(tf.square(target_y - predicted_y)) # Iteratively train the model by the set epoch number. The model will train adaptively by the gradient provided by the loss function with the selected optimizer. for i in range(epochs): with tf.gradient_tape() as t: loss = loss_mse(y_train, model(X_train)) train_loss = loss_mse(y_train, model(X_train)) test_loss = loss_mse(y_test, model(X_test)) print(f"""Epoch {i+1}: Training loss = {train_loss.numpy()}. Test loss = {test_loss.numpy()}""") jac = t.gradient(loss, model.trainable_weights) optimizer.apply_gradients(zip(jac, model.trainable_weights)) # To test the model, we'll setup a method to plot test set predictions ontop of the SPY price. def test_model(actual, title, X): prediction = model(X).numpy() prediction = prediction.reshape(-1, 1) plt.figure(figsize=(16, 6)) plt.plot(actual, label="Actual") plt.plot(prediction, label="Prediction") plt.title(title) plt.xlabel("Time step") plt.ylabel("SPY Price") plt.legend() plt.show() test_model(y_test, "Test Set Results from Original Model", X_test) # Store the model in the object store to allow accessing the model in the next research session or in the algorithm for trading. model_key = "model.keras" file_name = qb.object_store.get_file_path(model_key) model.save(file_name)

