Datasets
Forex
Create Subscriptions
Follow these steps to subscribe to a Forex security:
- Create a
QuantBook. - (Optional) Set the time zone to the data time zone.
- Call the
add_forexmethod with a ticker and then save a reference to the ForexSymbol.
qb = QuantBook()
qb.set_time_zone(TimeZones.UTC)
eurusd = qb.add_forex("EURUSD").symbol gbpusd = qb.add_forex("GBPUSD").symbol
To view all of the available Forex pairs, see Supported Assets.
Get Historical Data
You need a subscription before you can request historical data for a security. On the time dimension, you can request an amount of historical data based on a trailing number of bars, a trailing period of time, or a defined period of time. On the security dimension, you can request historical data for a single Forex pair, a subset of the pairs you created subscriptions for in your notebook, or all of the pairs in your notebook.
Trailing Number of Bars
To get historical data for a number of trailing bars, call the history method with the Symbol object(s) and an integer.
# DataFrame single_history_df = qb.history(eurusd, 10) subset_history_df = qb.history([eurusd, gbpusd], 10) all_history_df = qb.history(qb.securities.keys(), 10) # Slice objects all_history_slice = qb.history(10) # QuoteBar objects single_history_quote_bars = qb.history[QuoteBar](eurusd, 10) subset_history_quote_bars = qb.history[QuoteBar]([eurusd, gbpusd], 10) all_history_quote_bars = qb.history[QuoteBar](qb.securities.keys(), 10)
The preceding calls return the most recent bars, excluding periods of time when the exchange was closed.
Trailing Period of Time
To get historical data for a trailing period of time, call the history method with the Symbol object(s) and a timedelta.
# DataFrame of quote data (Forex data doesn't have trade data) single_history_df = qb.history(eurusd, timedelta(days=3)) subset_history_df = qb.history([eurusd, gbpusd], timedelta(days=3)) all_history_df = qb.history(qb.securities.keys(), timedelta(days=3)) # DataFrame of tick data single_history_tick_df = qb.history(eurusd, timedelta(days=3), Resolution.TICK) subset_history_tick_df = qb.history([eurusd, gbpusd], timedelta(days=3), Resolution.TICK) all_history_tick_df = qb.history(qb.securities.keys(), timedelta(days=3), Resolution.TICK) # Slice objects all_history_slice = qb.history(timedelta(days=3)) # QuoteBar objects single_history_quote_bars = qb.history[QuoteBar](eurusd, timedelta(days=3), Resolution.MINUTE) subset_history_quote_bars = qb.history[QuoteBar]([eurusd, gbpusd], timedelta(days=3), Resolution.MINUTE) all_history_quote_bars = qb.history[QuoteBar](qb.securities.keys(), timedelta(days=3), Resolution.MINUTE) # Tick objects single_history_ticks = qb.history[Tick](eurusd, timedelta(days=3), Resolution.TICK) subset_history_ticks = qb.history[Tick]([eurusd, gbpusd], timedelta(days=3), Resolution.TICK) all_history_ticks = qb.history[Tick](qb.securities.keys(), timedelta(days=3), Resolution.TICK)
The preceding calls return the most recent bars or ticks, excluding periods of time when the exchange was closed.
Defined Period of Time
To get historical data for a specific period of time, call the history method with the Symbol object(s), a start datetime, and an end datetime. The start and end times you provide are based in the notebook time zone.
start_time = datetime(2021, 1, 1) end_time = datetime(2021, 2, 1) # DataFrame of quote data (Forex data doesn't have trade data) single_history_df = qb.history(eurusd, start_time, end_time) subset_history_df = qb.history([eurusd, gbpusd], start_time, end_time) all_history_df = qb.history(qb.securities.keys(), start_time, end_time) # DataFrame of tick data single_history_tick_df = qb.history(eurusd, start_time, end_time, Resolution.TICK) subset_history_tick_df = qb.history([eurusd, gbpusd], start_time, end_time, Resolution.TICK) all_history_tick_df = qb.history(qb.securities.keys(), start_time, end_time, Resolution.TICK) # QuoteBar objects single_history_quote_bars = qb.history[QuoteBar](eurusd, start_time, end_time, Resolution.MINUTE) subset_history_quote_bars = qb.history[QuoteBar]([eurusd, gbpusd], start_time, end_time, Resolution.MINUTE) all_history_quote_bars = qb.history[QuoteBar](qb.securities.keys(), start_time, end_time, Resolution.MINUTE) # Tick objects single_history_ticks = qb.history[Tick](eurusd, start_time, end_time, Resolution.TICK) subset_history_ticks = qb.history[Tick]([eurusd, gbpusd], start_time, end_time, Resolution.TICK) all_history_ticks = qb.history[Tick](qb.securities.keys(), start_time, end_time, Resolution.TICK)
The preceding calls return the bars or ticks that have a timestamp within the defined period of time.
Wrangle Data
You need some historical data to perform wrangling operations. The process to manipulate the historical data depends on its data type. To display pandas objects, run a cell in a notebook with the pandas object as the last line. To display other data formats, call the print method.
DataFrame Objects
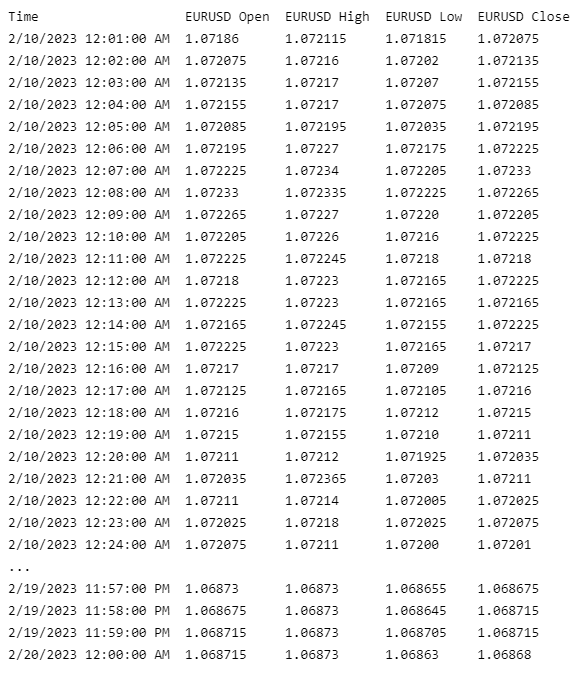
If the history method returns a DataFrame, the first level of the DataFrame index is the encoded Forex Symbol and the second level is the end_time of the data sample. The columns of the DataFrame are the data properties.
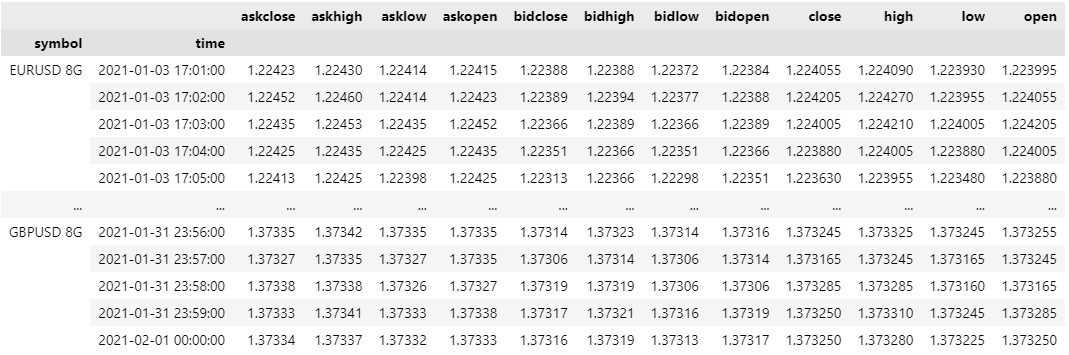
To select the historical data of a single Forex, index the loc property of the DataFrame with the Forex Symbol.
all_history_df.loc[eurusd] # or all_history_df.loc['EURUSD']
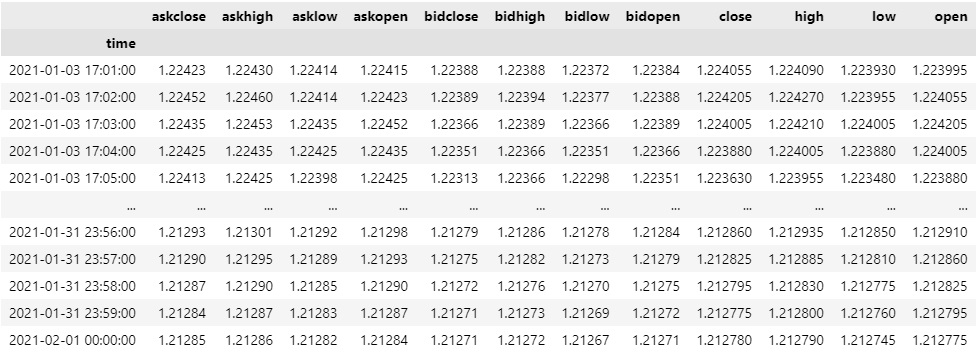
To select a column of the DataFrame, index it with the column name.
all_history_df.loc[eurusd]['close']
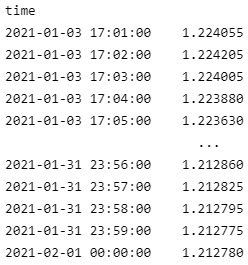
If you request historical data for multiple Forex pairs, you can transform the DataFrame so that it's a time series of close values for all of the Forex pairs. To transform the DataFrame, select the column you want to display for each Forex pair and then call the unstack method.
all_history_df['close'].unstack(level=0)
The DataFrame is transformed so that the column indices are the Symbol of each Forex pair and each row contains the close value.
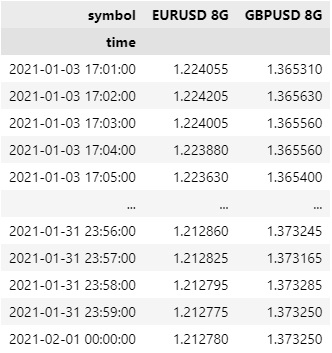
df["EURUSD close"]
Slice Objects
If the history method returns Slice objects, iterate through the Slice objects to get each one. The Slice objects may not have data for all of your Forex subscriptions. To avoid issues, check if the Slice contains data for your Forex pair before you index it with the Forex Symbol.
You can also iterate through each QuoteBar in the Slice.
for slice in all_history_slice: for kvp in slice.quote_bars: symbol = kvp.key quote_bar = kvp.value
QuoteBar Objects
If the history method returns QuoteBar objects, iterate through the QuoteBar objects to get each one.
for quote_bar in single_history_quote_bars: print(quote_bar)
If the history method returns QuoteBars, iterate through the QuoteBars to get the QuoteBar of each Forex pair. The QuoteBars may not have data for all of your Forex subscriptions. To avoid issues, check if the QuoteBars object contains data for your security before you index it with the Forex Symbol.
for quote_bars in all_history_quote_bars: if quote_bars.contains_key(eurusd): quote_bar = quote_bars[eurusd]
You can also iterate through each of the QuoteBars.
for quote_bars in all_history_quote_bars: for kvp in quote_bars: symbol = kvp.key quote_bar = kvp.value
Tick Objects
If the history method returns TICK objects, iterate through the TICK objects to get each one.
for tick in single_history_ticks: print(tick)
If the history method returns Ticks, iterate through the Ticks to get the TICK of each Forex pair. The Ticks may not have data for all of your Forex subscriptions. To avoid issues, check if the Ticks object contains data for your security before you index it with the Forex Symbol.
for ticks in all_history_ticks: if ticks.contains_key(eurusd): ticks = ticks[eurusd]
You can also iterate through each of the Ticks.
for ticks in all_history_ticks: for kvp in ticks: symbol = kvp.key tick = kvp.value
The Ticks objects only contain the last tick of each security for that particular timeslice
Plot Data
You need some historical Forex data to produce plots. You can use many of the supported plotting libraries to visualize data in various formats. For example, you can plot candlestick and line charts.
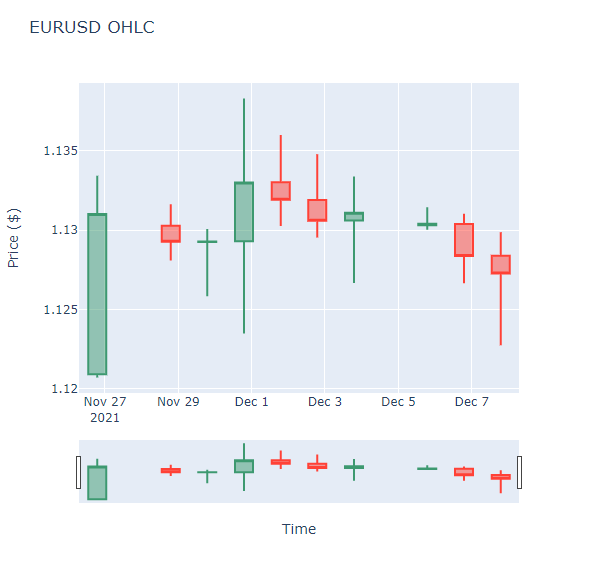
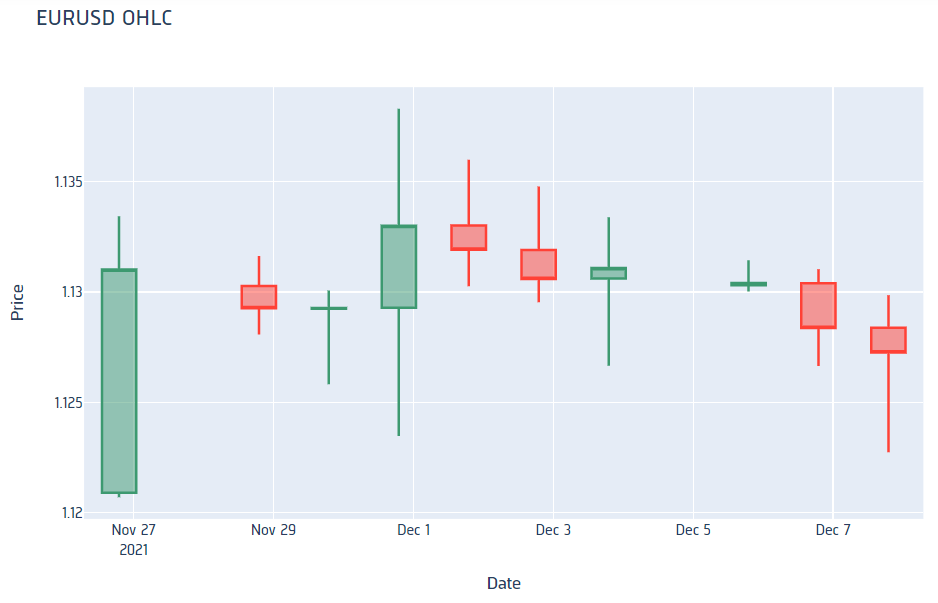
Candlestick Chart
Follow these steps to plot candlestick charts:
- Get some historical data.
- Import the
plotlylibrary. - Create a
Candlestick. - Create a
Layout. - Create the
Figure. - Show the
Figure.
history = qb.history(eurusd, datetime(2021, 11, 26), datetime(2021, 12, 8), Resolution.DAILY).loc[eurusd]
import plotly.graph_objects as go
candlestick = go.Candlestick(x=history.index, open=history['open'], high=history['high'], low=history['low'], close=history['close'])
layout = go.Layout(title=go.layout.Title(text='EURUSD OHLC'), xaxis_title='Date', yaxis_title='Price', xaxis_rangeslider_visible=False)
fig = go.Figure(data=[candlestick], layout=layout)
fig.show()
Candlestick charts display the open, high, low, and close prices of the security.
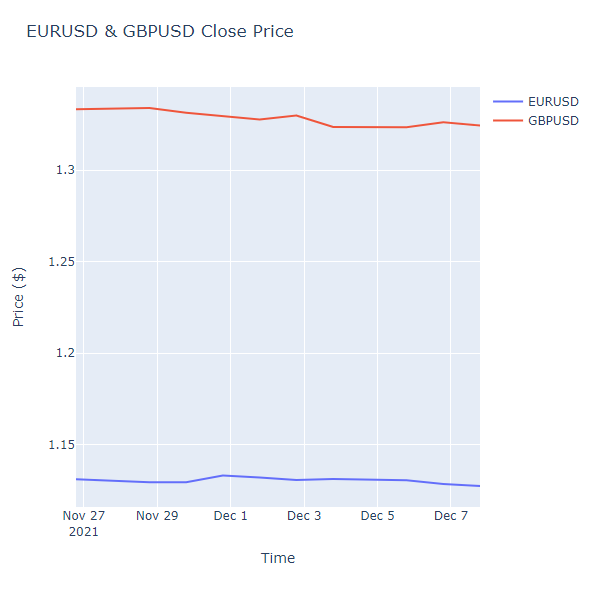
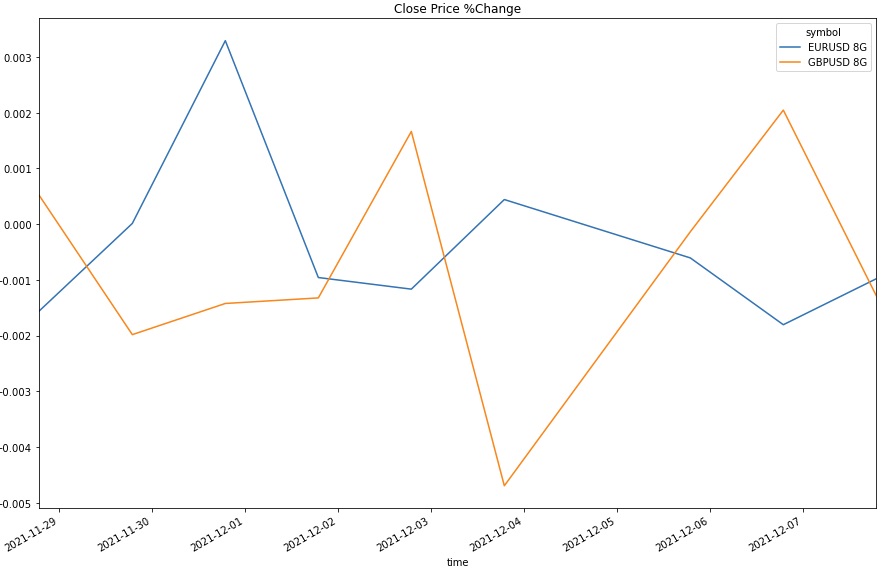
Line Chart
Follow these steps to plot line charts using built-in methods:
- Get some historical data.
- Select the data to plot.
- Call the
plotmethod on thepandasobject. - Show the plot.
history = qb.history([eurusd, gbpusd], datetime(2021, 11, 26), datetime(2021, 12, 8), Resolution.DAILY)
pct_change = history['close'].unstack(0).pct_change().dropna()
pct_change.plot(title="Close Price %Change", figsize=(15, 10))
plt.show()
Line charts display the value of the property you selected in a time series.
Examples
The following examples demonstrate some common practices for applying the Forex dataset.
Example 1: 5-Minute Candlestick Plot
The following example studies the candlestick pattern of the USDJPY. To study the short term pattern, we consolidate the data into 5 minute bars and plot the 5-minute candlestick plot, using the mid prices.
# Import plotly library for plotting. import plotly.graph_objects as go # Create a QuantBook qb = QuantBook() # Request USDJPY's historical data. symbol = qb.add_forex("USDJPY").symbol history = qb.history(symbol, start=qb.time - timedelta(days=182), end=qb.time, resolution=Resolution.MINUTE) # Drop level 0 index (Symbol index) from the DataFrame history = history.droplevel([0]) # Select the required columns to obtain the 5-minute OHLC data. history = history[["open", "high", "low", "close"]].resample("5T").agg({ "open": "first", "high": "max", "low": "min", "close": "last" }) # Crete the Candlestick chart using the 5-minute windows. candlestick = go.Candlestick(x=history.index, open=history['open'], high=history['high'], low=history['low'], close=history['close']) # Create a Layout as the plot settings. layout = go.Layout(title=go.layout.Title(text=f'{symbol} OHLC'), xaxis_title='Date', yaxis_title='Price', xaxis_rangeslider_visible=False) # Create the Figure. fig = go.Figure(data=[candlestick], layout=layout) # Display the plot. fig.show()